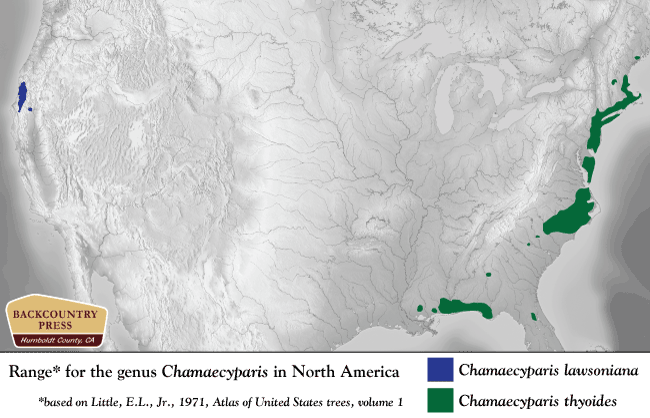
North America holds two of the most species-rich temperate forests in the world: those of the southern Appalachian and Klamath mountains. What do these locations have in common? Glaciers and seas did not completely cover them during the Cenozoic and the mountains were monadnocks, or islands above the plains, offering temperate refuges to plants and animals over time. Both locations have historically maintained a moderated climate. These areas are beyond the southern terminus of the enormous continental ice sheets of the Pleistocene. Some plants undoubtedly remained in these regions through historic climatic change, while other species repeatedly moved in as climate cooled and glaciers pushed southward and then moved out following glaciers northward. These dynamic fluctuations have cradled plant diversity in these two unique regions.
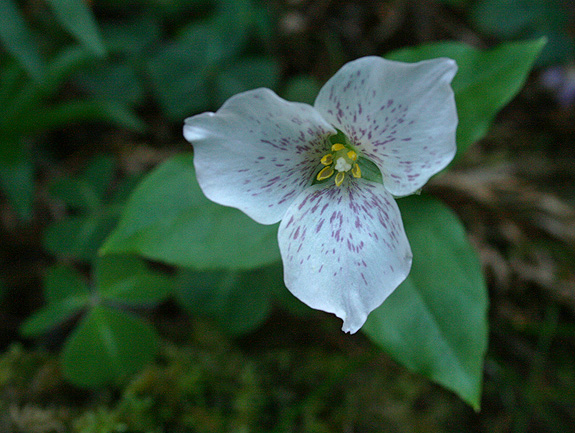
The current consequences of these historical patterns are that the Klamaths and southern Appalachians have grand floristic diversity, a concentration of endemic plants, and a fundamental importance to the forest floras of nearby regions (Whittaker 1960). Per unit area, the Klamath Mountains and the southern Appalachian Mountains hold more plant taxa than any others in North America. Plant genera such as Cornus (dogwoods), Asarum (wild ginger), and various conifers (Pinus, Abies, Thuja, Chamaecyparis) grow a continent apart while providing a comparative glimpse of an ancient flora.
-From Conifer Country
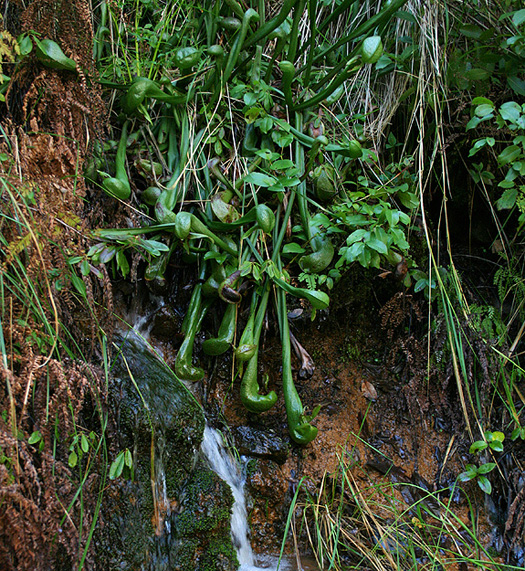
The Atlantic white-cedar (Chamaecyparis thyoides) and the Chester Cedar Swamp
My family and I made a Connecticut “migration” in July of 2014 to visit family near New York city. While I was looking forward to family time, I wondered if there could possibly be and natural, wild space anywhere near the largest population center in the country. A google search revealed that Connecticut does indeed have a few Natural Landmarks that preserve and celebrate the states geological and ecological heritage. I picked one to visit that was relatively close to our “home” as well as one that celebrates one of the most ancient lineages of plants on Earth – a conifer!