Part 2: Marble Mountain Wilderness
Read Part 1
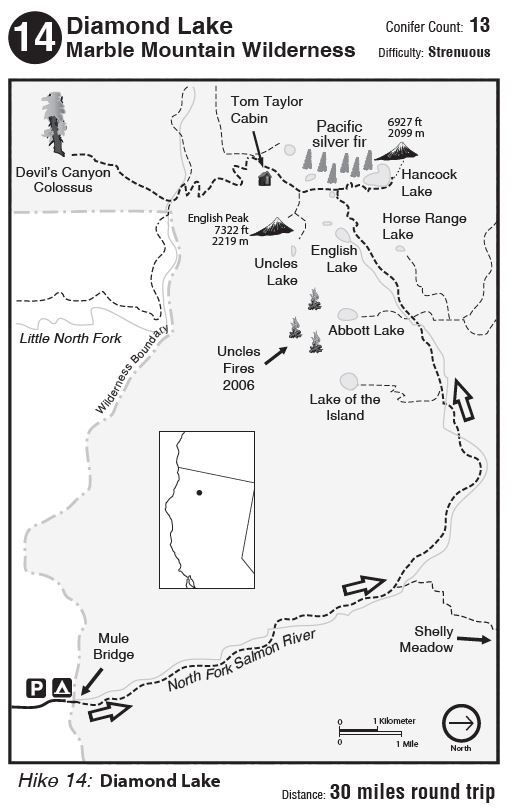
In conjunction with the Klamath National Forest and the California Native Plant Society Vegetation Team, I completed a mapping and inventory project for Pacific silver fir (Abies amabilis) in California. The first part of this project was along the Siskiyou Crest, near the Oregon-California border. This post is about the populations in the Marble Mountain Wilderness.
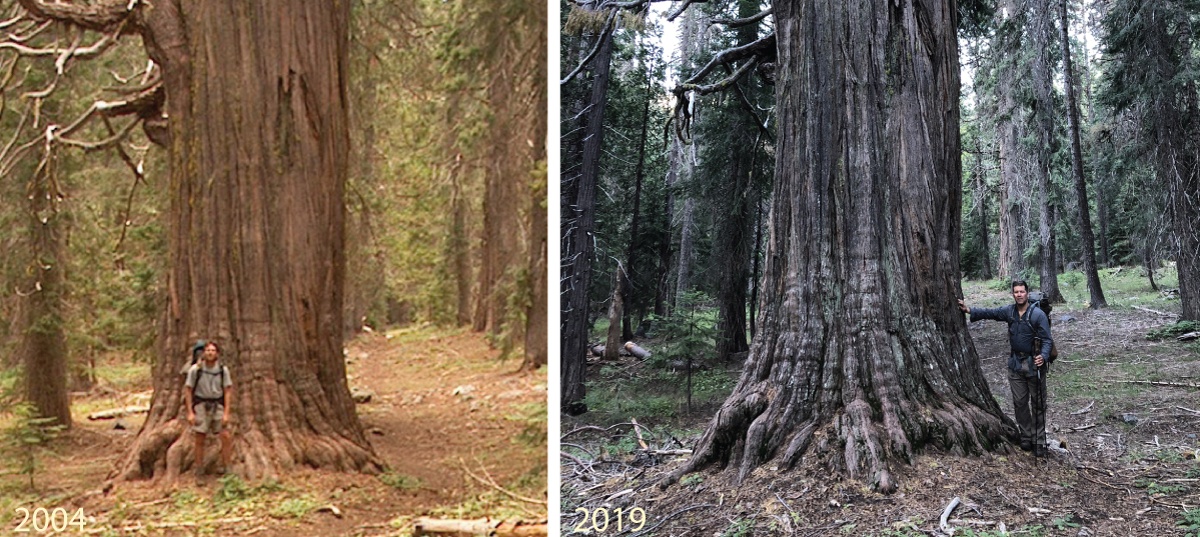
In 2016 I embarked on a mapping and inventory project for yellow-cedar (Callitropsis nootkatensis) in California. At the time, I called yellow-cedar California’s rarest conifer. In 2019, new discoveries on the north slopes of Copper Butte and Preston Peak brought the total hectares of yellow-cedar in California to ~21 hectares. With this new data, and that collected in this project, we now know Abies amabilis is California’s rarest conifer*! See table below for stand data summary.
*This excludes the neoendemic California cypresses.
Continue reading “Pacific Silver Fir in California”